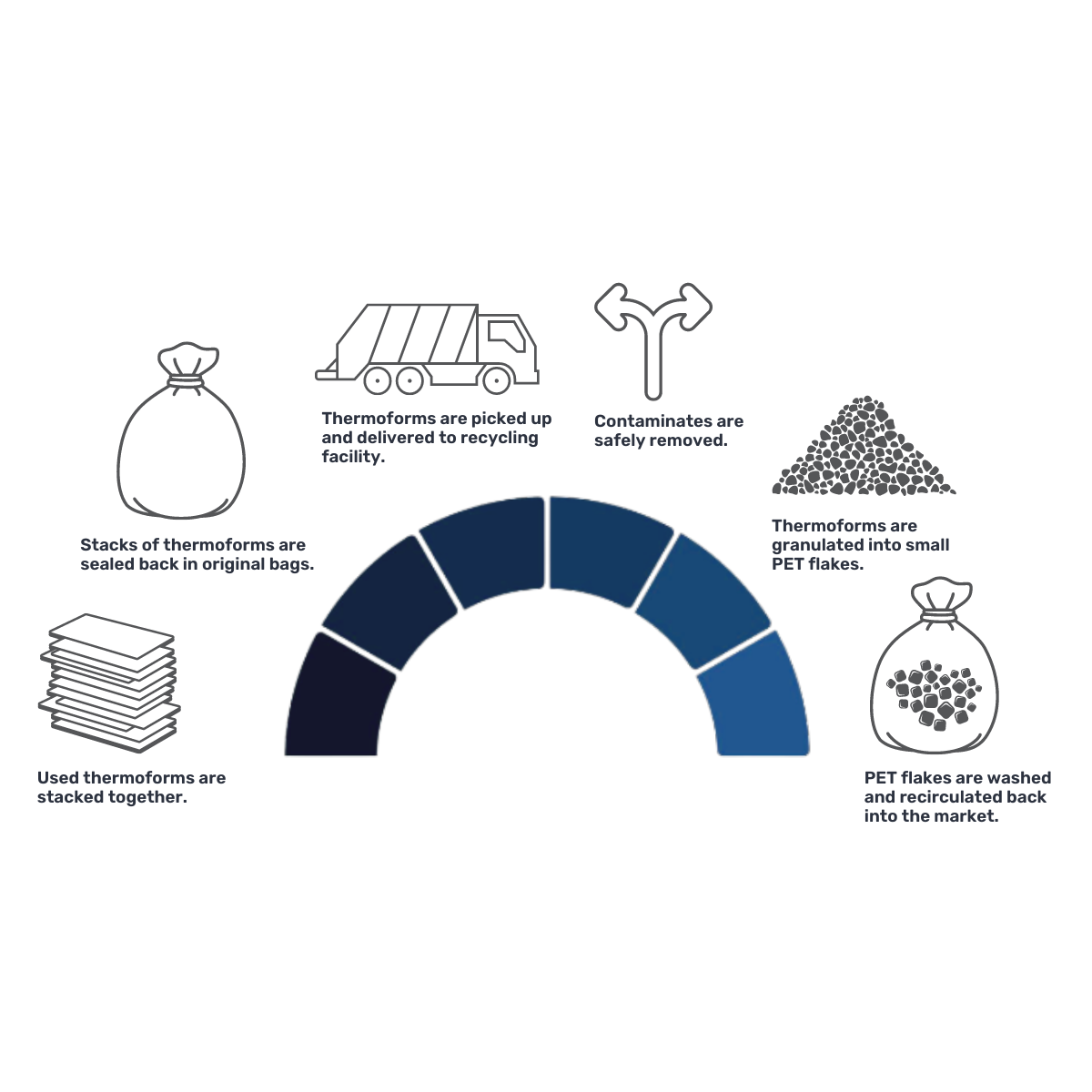
The Challenge
Creating End-of-life Solutions
Our customer, a global leader in laboratory research consumables, aspired to create a circular life cycle for their single-use polyethylene terephthalate (PET) thermoformed products. Labs in the life sciences represent a significant source of high quality, recyclable plastics which are often clean and uncontaminated. There is opportunity to unlock these sources by driving collection, and as a result, boost demand for high quality recycled content across end markets.
The Process
Performing a Life Cycle Assessment
Plastic Ingenuity partnered with a leading environmental consulting firm to determine the end-of-life recycling scenario with the lowest environmental impact for our customer’s thermoformed life science products. A closed-loop scenario involved recovering thermoforms from laboratories (end users), transporting to a centralized location for recycling, and incorporating the recovered flake into new thermoformed products for our customer. An open-market scenario involved sending used thermoforms to material reclamation facilities with closer proximity to end users, while incorporating post-consumer recycled (PCR) PET from the open market into new thermoformed products for our customer. PI conducted a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) to determine the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of logistics for each end-of-life scenario.
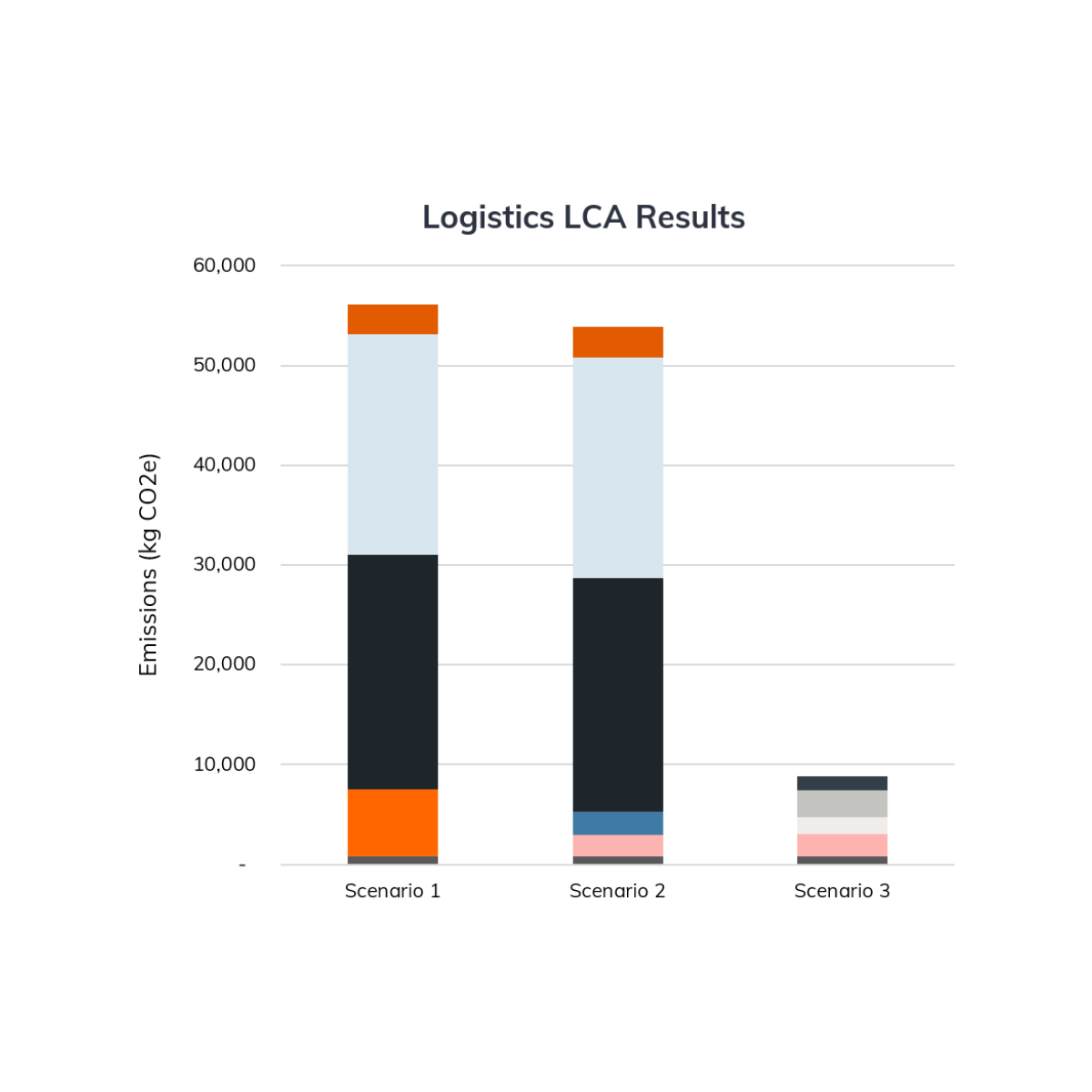
The Solution
Improved End-of-life Outcomes
Plastic Ingenuity found that a closed-loop scenario resulted in >6x more GHG emissions due to transportation alone. By setting recycled content targets upstream, driving collection, and infusing local recycling markets downstream, circularity can still be achieved and with a lower environmental impact.

The Results
Circularity with a Lower Environmental Impact
pounds of plastic diverted from landfills annually
reduction in GHG emissions from logistics
of the packaging that is recovered, is then recycled to make new products






