
Understanding the Language of Sustainability As the push for sustainable packaging grows,…

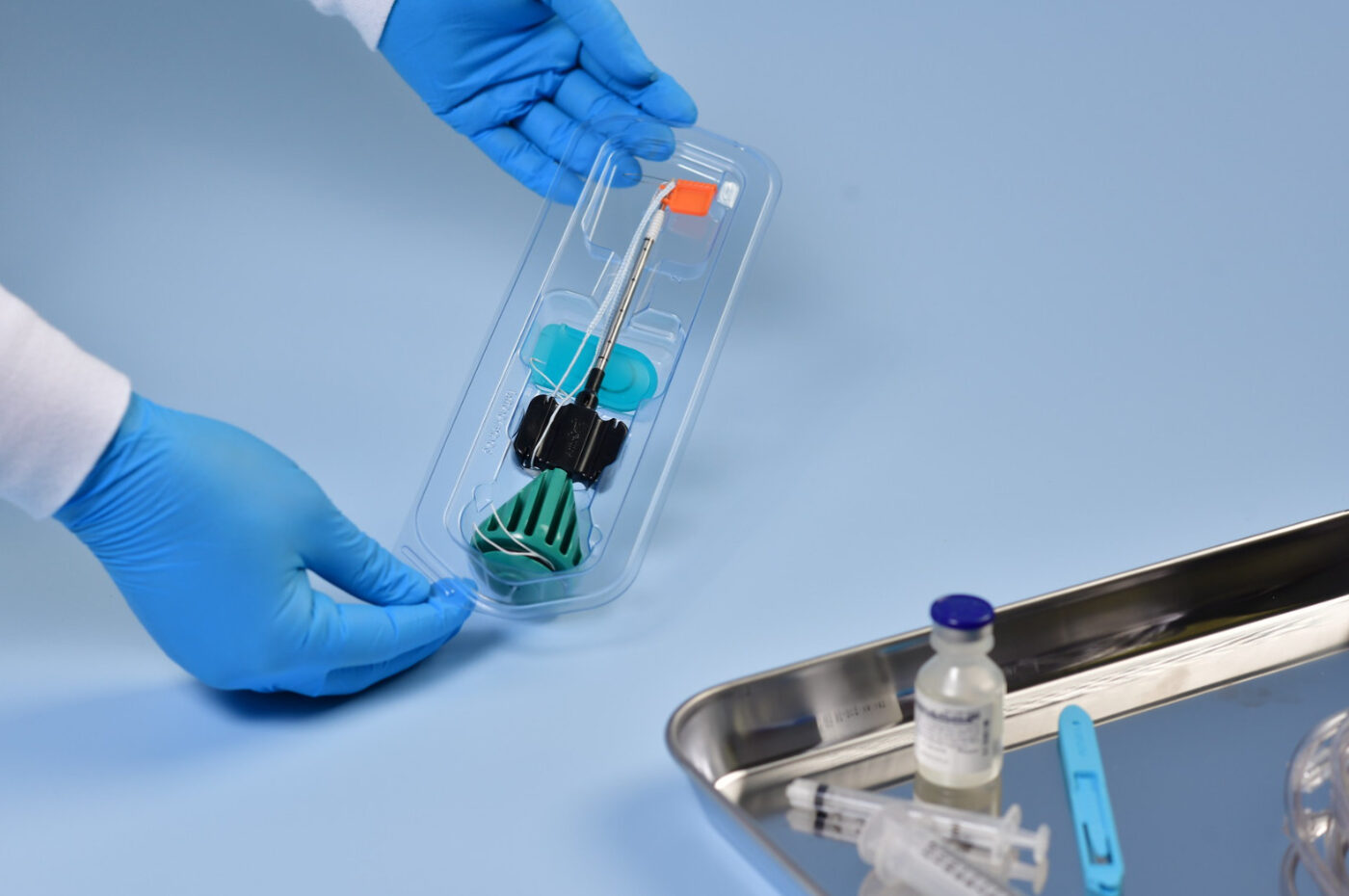
Sterile medical packaging plays a vital role in protecting patients from harmful bacteria and viruses. However, many processes can damage the integrity of sterile packaging as products move through the supply chain. Improper sterilization techniques, mishandling during shipping, and other mishaps can degrade packaging and cause loss of sterility. Regulatory agencies require all sterile packaging to undergo packaging validation to prevent these issues.
Packaging validation confirms that medical packaging maintains sterility and barrier integrity throughout the product’s lifetime. Federal regulations and industry standards require manufacturers to conduct validation testing before releasing products. This guide provides an in-depth look at packaging validation regulations, processes, and testing methods.
Packing validation ensures that healthcare manufacturers use proper packaging systems and sterilization methods throughout the manufacturing process. Packaging systems encase a broad range of sterile medical devices, including catheters, syringes, and surgical equipment. These systems consist of two parts:
Many sterilization and packaging processes can harm the sterile barrier system. For example, some polymer-based packaging materials will degrade and lose sterility if the manufacturer uses an inappropriate level of gamma radiation. Sterile barriers can also get damaged during assembly processes like cutting, capping, and sealing.
Packaging validation evaluates the performance of sterile barriers throughout manufacturing and distribution. This testing protects patient health by ensuring that products remain free of contaminants.
The Federal Drug Administration (FDA) oversees medical device package testing in the United States. The FDA has established numerous performance and safety standards for sterile medical packaging.
According to FDA regulations, manufacturers must test every batch or lot of sterile medical products to guarantee that the packaging maintains sterility during the entire shelf life. Additionally, the FDA requires companies to conduct stability testing to ensure that the sterile barrier remains intact when the packaging gets exposed to high temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors.
The International Organization for Standardization has also established global package validation requirements for medical devices. ISO 11607-2: 2019 provides guidelines for developing and validating sterile medical packaging systems. These regulations cover forming, sealing, and assembly processes.
Effective packaging validation strategies include these key components:
The validation process starts with selecting the right packaging for your product. Here are a few essential factors to consider:
A thermoforming expert at Plastic Ingenuity can help you choose the perfect packaging design and materials.
The FDA and ISO 11607 require manufacturers to conduct validation testing in several areas, including:
Additionally, manufacturers must provide the FDA with detailed information about the processing of sterile medical devices, including disinfection, storage, and transportation.
Packaging validation requirements for medical devices vary depending on the material and sterilization method used. Common testing methods include:
The FDA enforces compliance with medical device packaging validation procedures. An inspector reviews each product to ensure the chosen sterilization process fits the packaging requirements. They also examine the validation studies to ensure that the manufacturer follows appropriate testing parameters and uses properly calibrated equipment.
Packaging validation protects patients and providers from healthcare-associated infections and other risks associated with non-sterile medical devices.
Packaging validation is a complex but necessary process that keeps patients healthy. Manufacturers can ensure their medical device packaging remains sterile by choosing the proper materials, sterilization methods, and testing protocols. Fortunately, you don’t have to go through all these steps alone. Plastic Ingenuity is a leading manufacturer of thermoformed healthcare packaging. Our ISO 13485-certified team has decades of experience developing innovative packaging that complies with the latest regulations and validation testing techniques. Get in touch to learn how collaborating with Plastic Ingenuity can help you get your product to market quickly and safely.
Medical Review: Trager Hintze, PharmD
